Comp 283, 2025 Summer Session 1
Course Site for Comp 283
Algorithms
An algorithm is just a series of steps that return a result. They are usually used to help you get a more optimal result. (E.g. perform the task more accurately, faster, cheaper, etc.)
Day-to-day examples
Some common examples of algorithms you might use in your day-to-day are:
- Following a meal prep guide to help you eat healthier and save money.
- Following a routine in the gym to maximize your fitness goals.
- Choosing your class schedule to fit your preferences.
Anatomy of an Algorithm
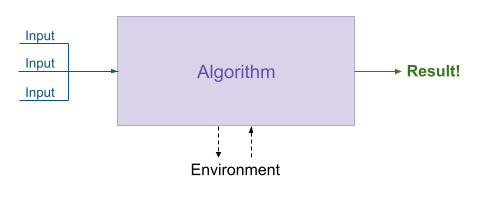
An algorithm is given at least one input,
it performs a series of steps,
and it returns a result.
Note that an algorithm may be influenced by its environment and it may produce side-effects which influence its environment. (I’ll give an example of this soon!)
Two important properities of an algorithm:
- it is finite
- it can handle an arbitrarily large input
Pseudocode
Sometimes, pseudocode can be helpful for expressing an algorithm! Pseudocode looks like code, but simplified and readable.
It is not meant to run on a computer, but rather it helps you outline what your algorithm is going to look like without going too bogged down in syntax.
You can reference your pseudocode to help you write actual code!
Example: Finding the low card in a deck
Say I want to describe an algorithm to find the lowest card in the deck of cards. The general steps are:
- Go from left to right
- Remember the lowest card you’ve seen so far and compare it to the next cards
In pseudocode, you could express it like this:
INPUT: deck of cards
lowest_card = first card in deck
for each card in the deck:
if current_card < lowest_card:
lowest_card = current_card
RETURN lowest_card
LS13: Algorithms
This activity will guide you through recognizing everyday algorithms, expressing them in structured logic, and beginning to justify them like a proof.
We will be sharing our favorite submissions on Edstem for a future assignment!
Please go to Gradescope to complete this assignment.
Example Submission
Part 1. Choose an Algorithm
What’s an example of an algorithm you use in your daily life? Think of anything with a step-by-step process, for example: picking your outfit, walking to class, choosing a YouTube video, ordering food, etc. Write 2–3 sentences describing what you do, in plain language.
Every night before bed, I decide what activity I want to do to relax. Sometimes I read a book, other times I watch TV, or I scroll on my phone. The choice depends on how I feel after the day and how much energy or time I have left.
Part 2. Identify Goals and Elements
What are you trying to optimize with this algorithm?
I would like to increase my ability to wind down and quality of sleep.
What are your inputs?
Difficulty of the day, energy levels, time of night
In general what are your steps? (In a very abstract sense.)
Evaluate how tired I feel
Estimate how much free time I have
Choose the activity that feels most suitable for my energy and time, while aiming to prioritize no screen time to improve my quality of sleep.
What are your outputs?
The activity I choose
How does this interact with the environment? (Is it impacted by its environment? Is it impacting its environment?)
This algorithm is impacted by my environment because it depends on what I have available (e.g. a good book, a charged phone, etc.). It impacts my environment by adding light to it if I’m choosing screentime, using power from my electronics, creasing the pages of my book, etc.
Part 3. Express in Pseudocode
Rewrite your description as a sequence of steps using algorithmic or logical language. Use words like:
If… then… Else While… For each… Return
If time_of_night is less than 30 minutes:
If energy_level is low:
Do "scroll on phone"
Else:
Do "watch TV"
Else:
If difficulty_of_day is high AND energy_level is low:
Do "watch TV"
Else if energy_level is high:
Do "read book"
Else:
Randomly choose between "read book" and "watch TV"
Part 4: Make a Claim and Justify It
Write a short claim about what your algorithm guarantees. It can be about its result or how it works.
This algorithm increases the likelihood that I read more often when I have the time and energy, while still adapting to days when I feel too tired.